Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) Programs
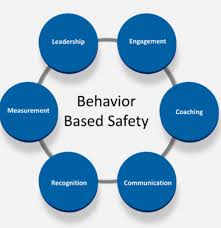
Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) is a proactive approach to workplace safety that focuses on observing, analyzing, and modifying the behaviors of employees to prevent accidents and injuries.
It recognizes that human behavior plays a critical role in workplace safety and seeks to create a culture where safety is a priority.
Key Components of a BBS Program:
- Observation: Trained observers conduct regular observations of employees’ behaviors, noting both safe and unsafe actions.
- Feedback: Observers provide timely and specific feedback to employees, reinforcing safe behaviors and addressing unsafe behaviors.
- Positive Reinforcement: Recognizing and rewarding safe behaviors to encourage their repetition.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing observation data to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Goal Setting: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) safety goals.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly reviewing and refining the BBS program to ensure its effectiveness.
Benefits of BBS Programs:
- Reduced Accidents and Injuries: By identifying and addressing unsafe behaviors, BBS programs can significantly reduce the number of workplace accidents and injuries.
- Improved Safety Culture: A strong safety culture is fostered by promoting safe behaviors and recognizing safe work practices.
- Increased Employee Engagement: Employees feel empowered to contribute to safety initiatives and take ownership of their safety.
- Enhanced Organizational Performance: A safer workplace can lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Cost Savings: Reduced costs associated with accidents, workers’ compensation claims, and lost productivity.
By implementing a well-designed BBS program, organizations can create a safer and more productive work environment.