Periodic Table Trends
The periodic table is a systematic arrangement of chemical elements, organized based on their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. Understanding periodic table trends is essential for predicting the behavior and properties of elements. These trends reveal patterns related to atomic size, ionization energy, electron affinity, and electronegativity, among others. Below is an overview of the key periodic table trends, their features, benefits, and why HNK Global is committed to advancing education in this crucial area of chemistry.
What Are Periodic Table Trends?
Periodic table trends refer to the predictable patterns in the properties of elements as you move across a period (row) or down a group (column) in the periodic table. These trends are influenced by the electron configuration of the elements and the effective nuclear charge experienced by electrons. Recognizing these trends helps scientists understand how elements interact with one another and how they can be used in chemical reactions.
Key Periodic Table Trends
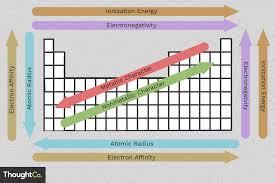
Atomic Radius
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electrons.- Trend Across a Period: The atomic radius decreases as you move across a period from left to right because the increased number of protons pulls electrons closer to the nucleus.
- Trend Down a Group: The atomic radius increases as you move down a group because additional electron shells are added, increasing the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons.
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom.- Trend Across a Period: Ionization energy increases as you move across a period because the nucleus has a stronger pull on the electrons, making it harder to remove them.
- Trend Down a Group: Ionization energy decreases as you move down a group because the outermost electrons are farther from the nucleus and more shielded by inner electrons, making them easier to remove.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity refers to an atom’s ability to attract and bond with electrons.- Trend Across a Period: Electronegativity increases across a period because the atoms have a stronger nuclear charge, attracting electrons more strongly.
- Trend Down a Group: Electronegativity decreases down a group as the atomic size increases, making it harder for atoms to attract electrons.
Electron Affinity
Electron affinity is the energy change when an atom gains an electron.- Trend Across a Period: Electron affinity becomes more negative (releases more energy) across a period as elements become more eager to gain electrons to achieve a stable configuration.
- Trend Down a Group: Electron affinity generally becomes less negative as you move down a group because the outer electrons are farther from the nucleus.
Metallic Character
Metallic character refers to how easily an element loses an electron and its tendency to form positive ions.- Trend Across a Period: Metallic character decreases as you move across a period because the elements become less willing to lose electrons.
- Trend Down a Group: Metallic character increases down a group as the atomic size increases and it becomes easier to lose electrons.
Benefits of Understanding Periodic Table Trends
Predicting Chemical Behavior
Understanding trends allows chemists to predict how elements will react with each other based on their position in the periodic table.Improved Chemical Bonding Knowledge
Periodic trends influence the types of bonds elements form (ionic, covalent, metallic) and the strength of these bonds.Material Design and Innovation
By understanding the trends, scientists can design materials with desired properties for specific uses, such as superconductors, catalysts, and semiconductors.Enhanced Learning and Education
Periodic trends are fundamental for students and researchers, helping them grasp key concepts of chemistry that apply to a wide range of chemical processes.Industrial and Technological Applications
Knowledge of trends aids in the development of new technologies, such as energy-efficient batteries, stronger materials, and environmentally friendly chemical processes.
Applications of Periodic Table Trends
Elemental Reactivity
Predicting how elements will interact with other substances, such as alkali metals reacting violently with water or halogens forming salts with metals.Chemical Engineering
Understanding periodic trends helps chemical engineers select appropriate elements for reactions and material production.Pharmaceuticals
The trends of elements can help in designing drugs that interact with the body in specific ways, especially when working with metals like zinc, iron, or copper.Environmental Chemistry
Periodic trends are important when studying elements that play a role in pollution or environmental degradation, such as metals in wastewater treatment.Energy Production
The study of trends in metals and semiconductors is crucial for designing energy-efficient devices, such as solar panels and fuel cells.
Why Choose HNK Global for Periodic Table Trends Education?
Comprehensive Learning Resources
HNK Global provides extensive resources on chemistry, including detailed guides on periodic table trends, helping learners understand the core concepts of the subject.Cutting-Edge Research
Our focus on research allows students and professionals to stay updated on the latest discoveries related to periodic trends and their practical applications.Interactive Educational Tools
We offer interactive tools and simulations to visualize periodic table trends, helping students to engage more deeply with the material.Expert Educators and Scientists
HNK Global collaborates with top educators and scientists to provide expert-led courses and insights into the chemistry of elements and periodic table trends.Global Networking Opportunities
By joining HNK Global’s educational network, students and professionals can connect with a global community dedicated to advancing chemistry knowledge.
The Future of Periodic Table Trends
The study of periodic table trends is far from static. New discoveries in chemistry, especially with the exploration of the periodic table’s extended elements, continue to provide deeper insights into the relationships between atomic structure and material properties. As technology evolves, the ability to manipulate elements based on periodic trends will lead to innovations in material science, environmental sustainability, and industrial applications. HNK Global is committed to leading the charge in educating the next generation of chemists, scientists, and engineers to harness the power of these trends for a better future.